Disability Risk Among Seniors 65-Plus
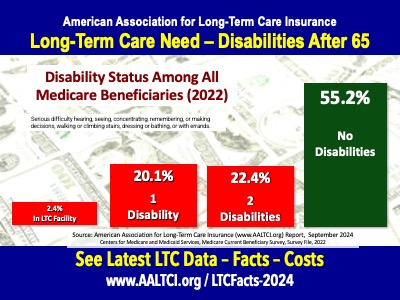 Almost half of Medicare beneficiaries have either one or two disabilities. The disability risk among seniors is important information for two reasons. The first is that disabilities are a key risk that aging Americans face resulting in the need for costly care. And second, because once someone has a disability, they generally can not qualify for long-term care insurance.
Almost half of Medicare beneficiaries have either one or two disabilities. The disability risk among seniors is important information for two reasons. The first is that disabilities are a key risk that aging Americans face resulting in the need for costly care. And second, because once someone has a disability, they generally can not qualify for long-term care insurance.
The latest data is highly relevant and important to share prior to turning 65 recommends the American Association for Long-Term Care Insurance. Living a long life means the likelihood of needing aide – and that’s where planning is important.
The data reflected seniors 65 and older who had difficulty hearing, seeing, remembering, dressing or bathing. These are Activities of Daily Living used to qualify for benefits under a traditional long-term care insurance policy.
Disability Risk Among Seniors 85-Plus
The risk of disabilities grows as one ages. Research indicates that among those aged 85 and older, approximately 25% have one disability.
Top-10 Disability Risk Among Seniors
The prevalence of disability among older adults is significantly influenced by various health conditions. As individuals age, they become more susceptible to chronic diseases and disabilities that can impact their daily functioning and quality of life. Based on the information provided, the following are the 10 leading causes of disability after age 65:
- Arthritis or Rheumatism: This condition affects joints and connective tissues, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. It is one of the most common causes of disability in older adults.
- Back or Spine Problems: Issues related to the back and spine, such as degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis, can result in chronic pain and limitations in movement.
- Heart Trouble: Cardiovascular diseases can lead to significant functional impairments due to heart failure or other heart-related issues.
- Lung or Respiratory Problems: Conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can severely limit physical activity and overall health.
- Mental or Emotional Problems: Mental health conditions such as depression or anxiety can affect cognitive function and daily activities.
- Diabetes: This metabolic disorder can lead to various complications that affect mobility and overall health.
- Deafness or Hearing Problems: Hearing loss can impact communication abilities and social interactions, contributing to isolation and disability.
- Blindness or Vision Problems: Visual impairments significantly affect independence and the ability to perform daily tasks safely.
- Stroke: A stroke can lead to long-term disabilities affecting mobility, speech, and cognitive functions.
- Cancer: Various types of cancer may cause disabilities either directly through the disease itself or indirectly through treatments that impair physical function.
LEARN MORE ABOUT LONG-TERM CARE INSURANCE PROTECTION. Get a free, no obligation quote for Long-Term Care Insurance from the American Association for Long-Term Care Insurance. Click here now!
INSURANCE AGENTS. SELL MORE LONG-TERM CARE INSURANCE PROTECTION. Visit the Association's Online LTC Learning, Marketing & Sales Center. Click here now!
HAVE YOU HEARD ABOUT CRITICAL ILLNESS INSURANCE? Learn more from the American Association for Critical Illness Insurance. Click here now!
MEDICARE SUPPLEMENT INSURANCE COSTS
Click here to learn more!